归并排序流程:
归并排序的基本思想是先将数组拆分后排序,再进行合并
例如一个数组[5,2,3,9],拆分后示意图如下:
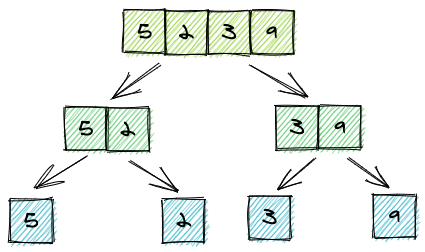
然后再进行合并,并且合并的过程中进行了排序:
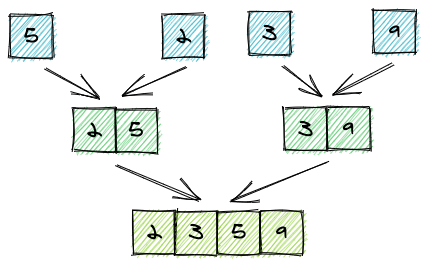
所以,拆分与合并很好理解,关键在于合并的过程中,如何进行排序。
例如2,5与3,9,合并过程如下:
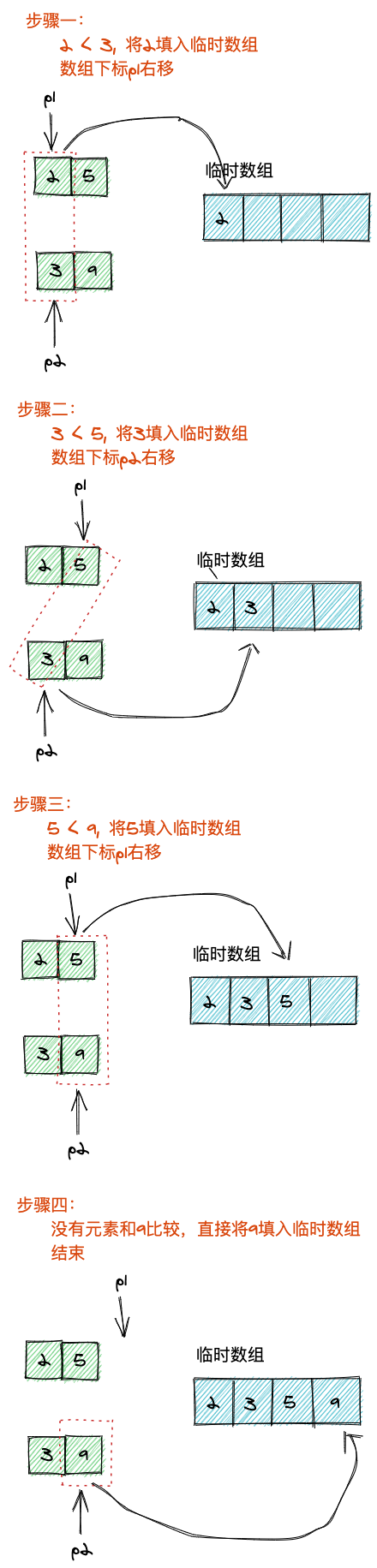
代码示例如下:
public class Merge {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] array = {4, 15, 8, 5, 7, 16, 3};
printArray(sort(array));
}
public static int[] sort(int[] sourceArray) {
//拷贝一份,不修改原数组
int[] array = Arrays.copyOf(sourceArray, sourceArray.length);
//拆分到数组元素小等于1时,就不用再拆分了
if (sourceArray.length <= 1) {
return array;
}
//对半拆分数组
int length = sourceArray.length / 2;
int[] array1 = Arrays.copyOfRange(array, 0, length);
int[] array2 = Arrays.copyOfRange(array, length, array.length);
System.out.print("拆分:");
printArray(array1);
System.out.print(" and ");
printArray(array2);
System.out.println("");
// 递归拆分并merge
return merge(sort(array1), sort(array2));
}
public static int[] merge(int[] array1, int[] array2) {
// 临时数组
int[] temp = new int[array1.length + array2.length];
int tempIndex = 0;
int index1 = 0, index2 = 0;
while (index1 < array1.length && index2 < array2.length) {
//两个数组两两比较,较小的值填入临时数组
if (array1[index1] < array2[index2]) {
temp[tempIndex++] = array1[index1++];
} else if (array1[index1] > array2[index2]) {
temp[tempIndex++] = array2[index2++];
} else {
// 值相等,可以都填入临时数组
temp[tempIndex++] = array1[index1++];
temp[tempIndex++] = array2[index2++];
}
}
// 走到这一步,其中一个数组的数据必然全部移到temp中
// 另一个数组元素如果还有剩余,则全部搬到temp中
while (index1 < array1.length) {
temp[tempIndex++] = array1[index1++];
}
while (index2 < array2.length) {
temp[tempIndex++] = array2[index2++];
}
System.out.print("合并:");
printArray(array1);
System.out.print(" and ");
printArray(array2);
System.out.print(" => ");
printArray(temp);
System.out.println("");
return temp;
}
public static void printArray(int[] array) {
for (int i = 0; i < array.length; i++) {
System.out.print(array[i] + " ");
}
}
}
执行结果:
拆分:4 15 8 and 5 7 16
拆分:4 and 15 8
拆分:15 and 8
合并:15 and 8 => 8 15
合并:4 and 8 15 => 4 8 15
拆分:5 and 7 16
拆分:7 and 16
合并:7 and 16 => 7 16
合并:5 and 7 16 => 5 7 16
合并:4 8 15 and 5 7 16 => 4 5 7 8 15 16
4 5 7 8 15 16 
